Custom GatedDeltaProduct Implementation
This directory contains a custom implementation of the GatedDeltaProduct layer, based on the Flash Linear Attention (FLA) library, with modifications specifically designed for time series forecasting tasks.
Overview
Our custom implementation adds hidden state weaving functionality that enables information to flow across encoder layers, maintaining temporal continuity - a crucial feature for time series forecasting that differs from the general-purpose language modeling focus of the official FLA implementation.
Reference
This implementation is based on:
- Official FLA Repository: https://github.com/fla-org/flash-linear-attention
- Original Paper: DeltaProduct: Improving State-Tracking in Linear RNNs via Householder Products (Siems et al., 2025)
What is DeltaProduct?
DeltaProduct is a linear RNN architecture that uses diagonal plus rank-nₕ state-transition matrices, formed as products of nₕ generalized Householder transformations. This provides a tunable mechanism to balance expressivity and efficiency compared to diagonal-only architectures like Mamba or GLA.
Key Concepts
- Householder transformations: Enable simultaneous token-channel mixing, overcoming the expressivity limitations of purely diagonal state-transition matrices
- Rank-nₕ structure: Allows better expressivity than rank-1 (DeltaNet) while maintaining training efficiency. The parameter
nₕ(number of Householder transformations) provides a tunable trade-off between expressivity and computational cost - Gated variant: Adds gating mechanisms for improved performance, allowing the model to control information flow through forget gates and output gates
Architecture Overview
DeltaProduct improves upon earlier linear RNN architectures:
- Diagonal architectures (Mamba, GLA, mLSTM): Use diagonal state-transition matrices for fast runtime but suffer from limited expressivity
- Rank-1 architectures (DeltaNet, RWKV-7): Use diagonal plus rank-1 structure, enabling simultaneous token-channel mixing with only a slight decrease in training efficiency
- DeltaProduct: Extends this to diagonal plus rank-nₕ structure, where multiple Householder transformations (nₕ ≥ 1) provide greater expressivity while maintaining computational efficiency
The architecture interprets DeltaNet's recurrence as performing one step of online gradient descent per token on an associative recall loss. DeltaProduct instead takes multiple (nₕ) steps per token, naturally leading to the rank-nₕ structure.
State Weaving Mechanism
Unlike DeltaProduct's original design for autoregressive language modeling, time series forecasting across a full horizon does not require causal masking. To exploit this property, we introduce state weaving, a mechanism that enables bidirectional information flow across the entire sequence length without additional parameters or computational overhead.
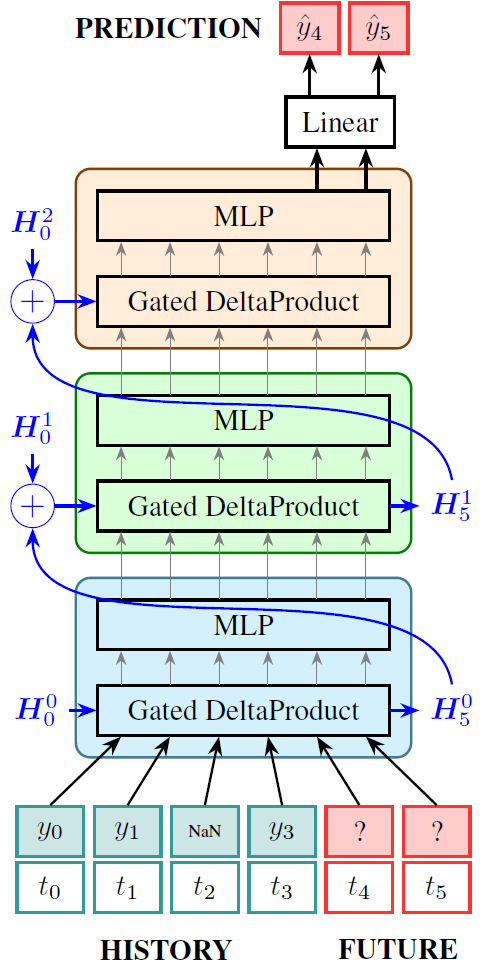
Figure: The TempoPFN architecture using stacked GatedDeltaProduct blocks with learnable initial states H₀ⁱ and state-weaving. The final hidden state of each layer Hₜⁱ is added to the learnable initial state of the next layer H₀ⁱ⁺¹, enabling bidirectional information flow.
How State Weaving Works
In our implementation, state weaving operates as follows:
Learnable Initial States: Each encoder layer
ihas a learnable initial hidden stateH₀ⁱthat is optimized during training.State Propagation: The final hidden state from layer
i, denotedHₜⁱ, is propagated forward and combined with the learnable initial state of the next layer:H₀ⁱ⁺¹ = H₀ⁱ⁺¹ + HₜⁱBidirectional Information Flow: This mechanism effectively lifts the causal constraint while maintaining computational efficiency. Information from later tokens can influence earlier layers through the accumulated hidden states, enabling the model to process the entire sequence (history + future horizon) coherently.
No Extra Overhead: Unlike explicit bidirectional architectures, state weaving requires no additional parameters or computational overhead beyond the existing forward pass.
This design is particularly powerful for time series forecasting, where:
- The full prediction horizon is known at inference time
- Coherent predictions across all future time steps are desired
- Historical context should inform all future predictions simultaneously
Key Differences from Official FLA
1. initial_state Parameter in Forward Method
Official FLA (fla/layers/gated_deltaproduct.py)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor | None = None,
past_key_values: Cache | None = None,
use_cache: bool | None = False,
output_attentions: bool | None = False,
**kwargs: Unpack[dict],
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor | None, Cache | None]:
No initial_state parameter - The official implementation only uses recurrent_state from past_key_values.
Our Custom Implementation (gated_deltaproduct.py)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
initial_state: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, # ← ADDED
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
**kwargs: Unpack[Dict],
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Cache]]:
Added initial_state parameter - Allows external control of the initial recurrent state, enabling layer-to-layer state propagation.
2. Usage of initial_state in Chunk Mode
Official FLA
if mode == 'chunk':
o, recurrent_state = chunk_gated_delta_product(
q=q, k=k, v=v, g=g, beta=beta,
initial_state=recurrent_state, # ← Only from past_key_values
output_final_state=use_cache,
cu_seqlens=cu_seqlens,
num_householder=self.num_householder,
use_qk_l2norm_in_kernel=True,
)
Our Custom Implementation
if mode == "chunk":
o, recurrent_state = chunk_gated_delta_product(
q=q, k=k, v=v, g=g, beta=beta,
initial_state=initial_state, # ← Uses external initial_state if provided
output_final_state=output_attentions,
cu_seqlens=cu_seqlens,
num_householder=self.num_householder,
use_qk_l2norm_in_kernel=True,
)
Key Difference: Our implementation prioritizes the externally provided initial_state over recurrent_state from past_key_values, enabling layer-to-layer state propagation.
3. Return Value: Hidden State Output
Official FLA (fla/models/gated_deltaproduct/modeling_gated_deltaproduct.py)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: torch.Tensor | None = None,
past_key_values: Cache | list[torch.FloatTensor] | None = None,
use_cache: bool | None = False,
output_attentions: bool | None = False,
**kwargs: Unpack[dict],
) -> tuple[torch.FloatTensor, tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor] | None]:
# ...
return outputs # Returns (hidden_states, attentions, past_key_values)
No initial_state parameter - The block doesn't accept or return hidden states explicitly.
Our Custom Implementation (modeling_gated_deltaproduct.py)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Union[Cache, List[torch.FloatTensor]]] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
initial_state: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None, # ← ADDED
**kwargs: Unpack[Dict],
) -> Tuple[
torch.FloatTensor, Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]
]:
# ...
hidden_states, attentions, past_key_values = self.attn(
# ...
initial_state=initial_state, # ← Passed through
**kwargs,
)
# ...
return outputs # Returns (hidden_states, attentions, past_key_values)
Added initial_state parameter - The block accepts and forwards initial_state to the attention layer.
4. Hidden State Weaving Implementation
Our implementation supports two modes of hidden state weaving (controlled by the weaving parameter in encoder config):
Mode 1: Weaving Enabled (weaving=True) - Default
if self.encoder_config.get("weaving", True):
# initial hidden state is learnable
hidden_state = torch.zeros_like(
self.initial_hidden_state[0].repeat(batch_size * num_channels, 1, 1, 1)
)
for layer_idx, encoder_layer in enumerate(self.encoder_layers):
x, hidden_state = encoder_layer(
x,
hidden_state + self.initial_hidden_state[layer_idx].repeat(
batch_size * num_channels, 1, 1, 1
),
)
Key Features:
- Hidden state accumulates across layers
- Each layer receives:
previous_hidden_state + learnable_initial_state[layer_idx] - State persists between layers, allowing information to flow through the network
Mode 2: No Weaving (weaving=False)
else:
# initial hidden state is separately learnable for each layer
for layer_idx, encoder_layer in enumerate(self.encoder_layers):
initial_hidden_state = self.initial_hidden_state[layer_idx].repeat(
batch_size * num_channels, 1, 1, 1
)
x, _ = encoder_layer(x, initial_hidden_state)
Key Features:
- Each layer uses its own independent learnable initial state
- No accumulation between layers
- Hidden state is discarded after each layer
5. Learnable Initial Hidden States
Our implementation includes learnable initial states managed at the model level:
num_initial_hidden_states = self.num_encoder_layers
self.initial_hidden_state = nn.ParameterList(
[
nn.Parameter(
torch.randn(
1, self.encoder_config["num_heads"], head_k_dim, head_v_dim
)
/ head_k_dim,
requires_grad=True,
)
for _ in range(num_initial_hidden_states)
]
)
Key Features:
- One learnable parameter per encoder layer
- Shape:
[1, num_heads, head_k_dim, head_v_dim] - Initialized with small random values scaled by
head_k_dim - These are trainable parameters that can be optimized during training
6. Parameter Name Differences
- Official FLA: Uses
use_output_gateparameter - Our Implementation: Uses
use_gateparameter (renamed for clarity)
7. Return Value Differences
Official FLA (fla/layers/gated_deltaproduct.py)
return o, None, past_key_values # Returns (output, None, past_key_values)
Our Custom Implementation (gated_deltaproduct.py)
return o, recurrent_state, past_key_values # Returns (output, recurrent_state, past_key_values)
Key Difference: Our implementation returns recurrent_state (the final hidden state) instead of None, enabling state propagation.
8. Encoder Wrapper Return Values
Our GatedDeltaProductEncoder (in src/models/blocks.py) returns both the output and hidden state:
x, last_hidden_state, _ = self.encoder_layer(
x, output_attentions=True, initial_state=initial_state
)
return x, last_hidden_state # ← Returns hidden state for weaving
This allows state propagation between layers in the TimeSeriesModel.
Summary Table
| Feature | Official FLA | Our Custom Implementation |
|---|---|---|
initial_state in forward() |
❌ No | ✅ Yes |
initial_state in GatedDeltaProductBlock.forward() |
❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Hidden state weaving | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (configurable) |
| Learnable initial states | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (nn.ParameterList) |
Returns recurrent_state |
❌ No (returns None) |
✅ Yes |
| Layer-to-layer state propagation | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (when weaving=True) |
| Parameter name | use_output_gate |
use_gate |
Why These Differences Matter for Time Series Forecasting
Temporal Continuity: Hidden state weaving allows information to flow across layers, maintaining temporal patterns across the encoder stack. This is crucial for time series where historical context matters.
Learnable Initialization: Learnable initial states allow the model to learn optimal starting points for the recurrent computation, which can be crucial for capturing time series patterns.
Flexible State Management: The
weavingparameter allows switching between:- Weaving mode: Better for capturing long-term dependencies across layers
- Independent mode: Each layer processes independently, potentially more stable
State Propagation: Returning and propagating hidden states enables the model to maintain context across multiple encoder layers, which is beneficial for time series forecasting where historical context matters.
These modifications make our implementation better suited for time series forecasting tasks compared to the general-purpose language modeling focus of the official FLA implementation.
Files in This Directory
gated_deltaproduct.py: Core GatedDeltaProduct layer implementation withinitial_statesupportmodeling_gated_deltaproduct.py: GatedDeltaProductBlock wrapper that integrates the layerconfiguration_gated_deltaproduct.py: Configuration class for the model__init__.py: Module exports
Usage
See src/models/model.py and src/models/blocks.py for examples of how to use this custom implementation with hidden state weaving.
To enable/disable weaving, set the weaving parameter in your encoder configuration:
encoder_config = {
"weaving": True, # Enable state propagation across layers
# ... other config parameters
}